This document describes a standard way of recording colour marks (combinations
of colour rings, colour rings with enscriptions, multi-coloured rings,
leg flags, neck collars, wing tags, nasal tags and saddles...). Many
thanks to Alain Fosse for putting together this web page to better show
the use of the coding standard (link).
Some of the text is in French and English.
See illustrations of colour marks on the web site produced by Holmer
Vonk :
http://www.holmer.nl/birdrings.htm
Colour codes
| R = red
W = white
G = dark green
L = light green (lime)
M = metal ring
Y = yellow
P = pale blue |
O = orange
C = dark pink (carmine)
K = light pink
B = dark blue
U = brown
V = violet/mauve/purple
S = grey/silver
A = other metal ring |
1. Legs
11. Rings
111. Which leg (L = gauche/left, R = droit/right)
112. Position on the leg either above or below the tarsal joint (B
= tarse/below, A = tibia/above)
we have
LB = left tarsus
LA = left tibia
RB = right tarsus
RA = right tibia
The leg codes are separated by a semicolon
?B = tarsus (side unknown), ?A = tibia (side unknown)
113. in order of height from the top down the colours are separated
by commas
114. If there is an inscription then following the colour ring code
another colour code gives the colour of the inscription followed by the
code enclosed within parentheses (bars around the ring are shown by the
"/" character).
.gif) = LAM;RBWN(509X)
= LAM;RBWN(509X) 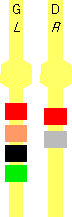 =
LBR,O,N,L;RBR,M =
LBR,O,N,L;RBR,M
.gif) = LBM;RBGW(X/9)
= LBM;RBGW(X/9).gif) = LAM;RBRW(/L9/)
= LAM;RBRW(/L9/)
115. two colour rings
2 = two colour striped rings (top colour given first)
3 = two colours side-by-side (top colour given first)
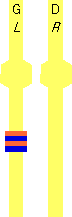 = LBOB2
= LBOB2.gif) = LBOB2N(A8)
= LBOB2N(A8)
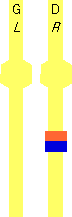 = RBOB3
= RBOB3
12. Leg flags
F = flag
See for example http://www.mb.ec.gc.ca/nature/migratorybirds/pasp/dc29s01.fr.html
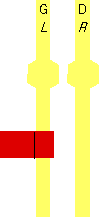 =
LBRF =
LBRF
 = LAOF;RAM;RBR,Y
= LAOF;RAM;RBR,Y
Copyright: Hugh Insley
13. large rings
131. simple
T = tall, the ring made twice the height of a
normal ring
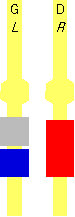 =
LBM,B;RBRT =
LBM,B;RBRT
132. wasp rings
= #, and within parentheses coded values for the width of
the bands :
1 = narrow, 2 = wide, 0 = no band (the character
before the parentheses indicates the colour of the bands).
.gif) =
LAM;RBY#N(111) =
LAM;RBY#N(111) .gif) =
LBM;RBY#N(102) =
LBM;RBY#N(102)
2. Neck
NC = neck collar
.gif)
3. Wing
RW = right wing tag
LW = left wing tag
example : RWO,B;LWN,W = right
tag with orange at the front and blue at the back, left tag black and white
4. Bill
NS = nasal tag or saddle
example : NSRB(QQ) = red saddle
with blue "QQ"
see pictures: http://www.holmer.nl/nasal_marks.htm
Shapes
[Q] = square [R] = rectangle
[T] =
triangle [C] = circle
[H] = hexagon [O] = octagon [S] =
star
example : NSR[Q],G[C] = red square
tage in the right and green circular tag on the left
5. Sighting uncertanties
Colour mark observations can be difficult and some details
cannot always be seen. An incomplete sight record may still be of value.
In this case a question mark can be used to indicate some uncertainty
in colour or even position :
?B = tarsus (side not noted), ?A = tibia (side
not noted)
LBO?(AHT) = colour of the enscription not discerned
|
.gif) = LAM;RBWN(509X)
= LAM;RBWN(509X) 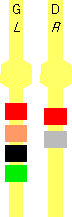 =
LBR,O,N,L;RBR,M
=
LBR,O,N,L;RBR,M
.gif) = LBM;RBGW(X/9)
= LBM;RBGW(X/9).gif) = LAM;RBRW(/L9/)
= LAM;RBRW(/L9/)
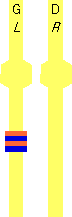 = LBOB2
= LBOB2.gif) = LBOB2N(A8)
= LBOB2N(A8)
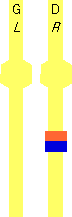 = RBOB3
= RBOB3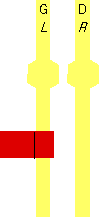 =
LBRF
=
LBRF
 = LAOF;RAM;RBR,Y
= LAOF;RAM;RBR,Y
 =
LBM,B;RBRT
=
LBM,B;RBRT.gif) =
LAM;RBY#N(111)
=
LAM;RBY#N(111) .gif) =
LBM;RBY#N(102)
=
LBM;RBY#N(102).gif)